Types of Keywords in SEO: A Detailed Overview
Understanding the types of keywords in Search Engine Optimization (SEO) is critical for formulating an effective online strategy. This article provides an in-depth look at the various keyword types and their significance in attracting traffic, enhancing search rankings, and boosting overall visibility.
1. What Are Keywords in SEO?
Keywords are the specific words and phrases that users enter into search engines when looking for information. They act as a connection between user queries and the relevant content available online. Identifying and utilizing the right keywords can significantly improve our visibility in search engine results pages (SERPs).
2. Types of Keywords
2.1. Short-Tail Keywords
Short-tail keywords are typically one or two words and are quite broad. Examples include “shoes” or “digital marketing.” While these keywords attract a high search volume, they are often too general, leading to less targeted traffic.
2.2. Long-Tail Keywords
Long-tail keywords consist of three or more words and are more specific. For instance, phrases like “best running shoes for flat feet” or “digital marketing strategies for small businesses.” Although they usually have lower search volumes, they tend to produce higher conversion rates by targeting users who are further along in the buying journey.
2.3. Exact Match Keywords
Exact match keywords refer to phrases that precisely match the user’s search query. For example, if someone types “buy red shoes online,” that phrase would be an exact match. While they can improve relevancy, relying solely on them can limit the diversity of your keyword strategy.
2.4. Phrase Match Keywords
Phrase match keywords allow for additional words before or after the keyword phrase while keeping the exact order of words. For example, “red shoes for sale” would match a search for “best red shoes for sale online.” This approach enables us to capture a broader audience while still maintaining relevance.
2.5. Broad Match Keywords
Broad match keywords allow for a wider interpretation of search queries. Using the keyword “shoes” might trigger results for related terms like “buy shoes” or “running shoes.” While this can generate significant traffic, it often leads to less targeted visitors, making careful monitoring necessary.
2.6. Negative Keywords
Negative keywords are those for which we do not want our ads to appear. Using negative keywords helps filter out irrelevant traffic. For instance, if we sell luxury shoes, we might exclude terms like “cheap” or “discount” to avoid attracting users who are not part of our target audience. This strategy improves ad relevance and optimizes marketing budgets.
3. The Importance of Keyword Research
Keyword research forms the foundation of any successful SEO strategy. Understanding which keywords are most relevant to our audience allows us to create tailored content. Tools such as Google Keyword Planner, Ahrefs, and SEMrush provide valuable insights into search volume, competition, and related terms.
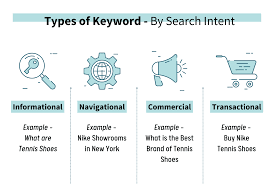
3.1. Identifying User Intent
It’s crucial to align keywords with user intent—the underlying goal of a search. User intent can generally be categorized into four types:
- Informational: Users seeking information (e.g., “What are the benefits of running?”).
- Navigational: Users looking for a specific website (e.g., “Nike official site”).
- Transactional: Users ready to make a purchase (e.g., “buy running shoes”).
- Commercial Investigation: Users comparing options before purchasing (e.g., “best running shoes for women”).
Aligning our content with these intents can enhance engagement and improve conversion rates.
4. Implementing Keywords in Your Content Strategy
Once the appropriate keywords are identified, the next step is to incorporate them into our content effectively.
4.1. On-Page SEO
Integrating keywords into on-page elements is vital. This includes:
- Title Tags: Ensure the primary keyword is included in the title.
- Meta Descriptions: Write compelling meta descriptions that incorporate keywords to improve click-through rates.
- Headers: Use keywords in subheadings (H2, H3) to enhance content organization and relevance.
- Body Content: Naturally integrate keywords throughout the article, avoiding keyword stuffing.
4.2. Content Length and Quality
Longer, high-quality content typically ranks better on search engines. Aim for at least 1,000 words, ensuring the content is informative and engaging while meeting the audience’s needs. Use keywords naturally throughout the piece.
4.3. Internal and External Links
Including both internal links (to other relevant content on your site) and external links (to authoritative sources) enhances credibility and provides added value to users. This practice can also improve SEO performance by encouraging search engines to crawl your site more effectively.
5. Conclusion
In summary, understanding the types of keywords in SEO is essential for developing an effective digital strategy. By employing a mix of short-tail, long-tail, exact, phrase, broad match, and negative keywords, we can attract high-quality traffic and optimize our conversion opportunities. Keyword research and implementation are critical, and aligning content with user intent will ultimately enhance engagement and improve rankings.
Related:







