Introduction
As our world becomes increasingly digital, the importance of data security continues to rise. Organizations face a multitude of cyber threats that can lead to significant financial losses and reputational damage. In this context, penetration testing (often referred to as pentesting) emerges as a vital strategy for identifying and addressing security vulnerabilities within information systems. This article provides an in-depth look at penetration testing, its significance, and its various components.
Learning Objectives
This article aims to equip readers with essential knowledge regarding penetration testing. By the end, readers will be able to:
- Define penetration testing and understand its critical role in cybersecurity.
- Identify the different types of penetration tests and their specific applications.
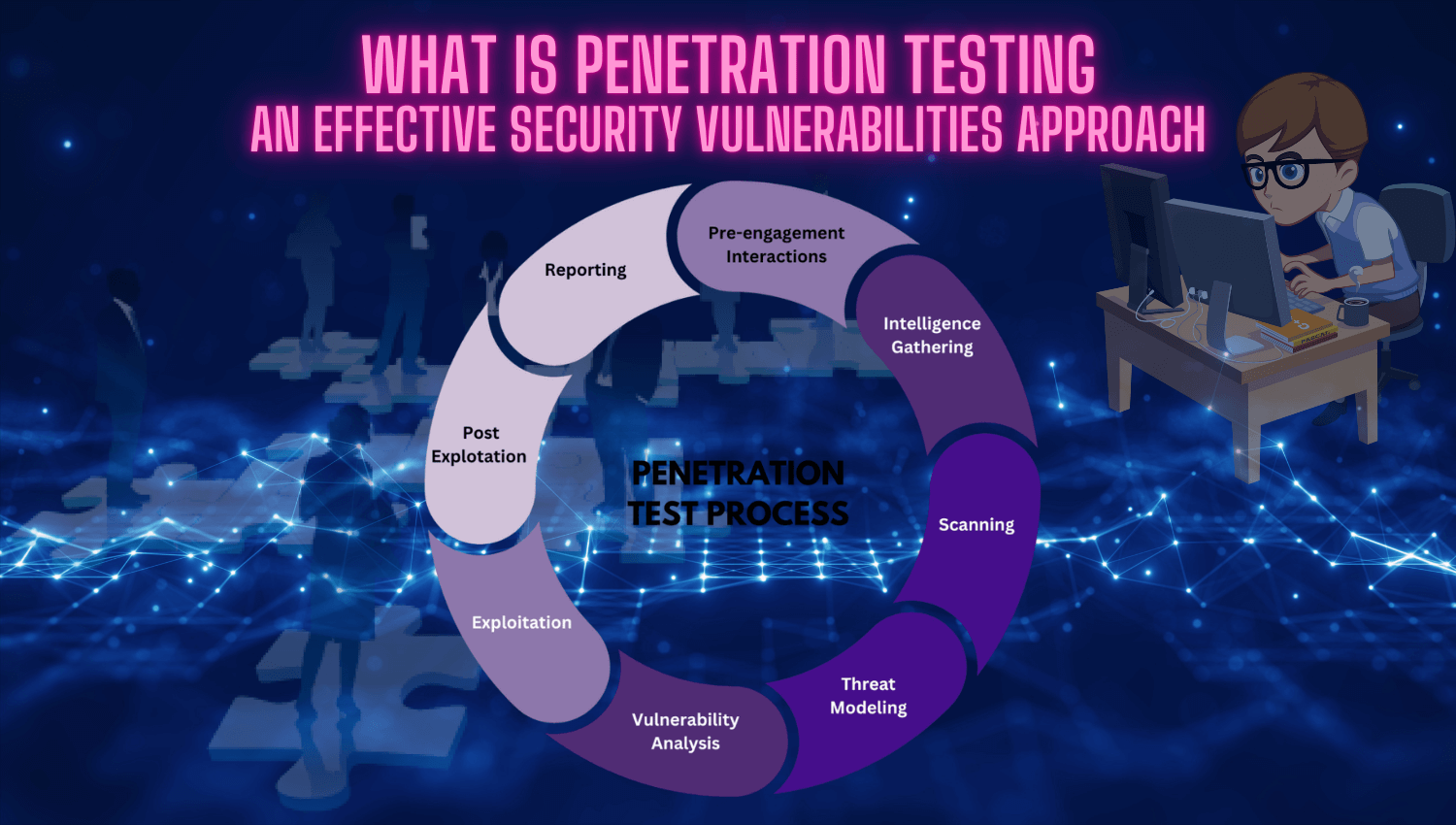
- Comprehend the structured phases involved in the penetration testing process.
- Explore the tools commonly used by ethical hackers during assessments.
- Evaluate the results of penetration tests and develop actionable remediation strategies.
What is Penetration Testing?
Penetration testing is a systematic approach that involves simulating cyberattacks on an organization’s systems to uncover vulnerabilities that could be exploited by malicious actors. Conducted by ethical hackers or security professionals, these tests aim to assess the effectiveness of existing security measures and identify areas for improvement. By proactively identifying weaknesses, organizations can bolster their defenses against potential cyber threats and safeguard sensitive data.
Types of Penetration Testing
Penetration tests can be categorized into three primary types, each serving distinct purposes:
- Black Box Testing: In this approach, testers have no prior knowledge of the system being tested. This method simulates an external attacker’s perspective, allowing organizations to evaluate how well their defenses hold up against real-world threats.
- White Box Testing: Here, testers are provided with complete access to the system’s internal workings, including source code and architecture. This comprehensive evaluation helps identify vulnerabilities that may not be apparent from an external viewpoint.
- Gray Box Testing: This hybrid approach combines elements of both black box and white box testing. Testers possess limited knowledge about the system, enabling them to simulate both internal and external threats effectively. Gray box testing often provides a balanced assessment of an organization’s security posture.
Conclusion
In conclusion, penetration testing is an essential practice for organizations aiming to enhance their cybersecurity measures. By regularly conducting these tests, organizations can identify and remediate vulnerabilities before they can be exploited by attackers. Additionally, penetration testing helps ensure compliance with various regulatory standards that mandate regular security assessments.For those seeking a deeper understanding of penetration testing—its processes, tools, and best practices—please refer to the full article available here. This comprehensive guide offers valuable insights for both cybersecurity professionals and organizational leaders looking to strengthen their defenses against cyber threats.







