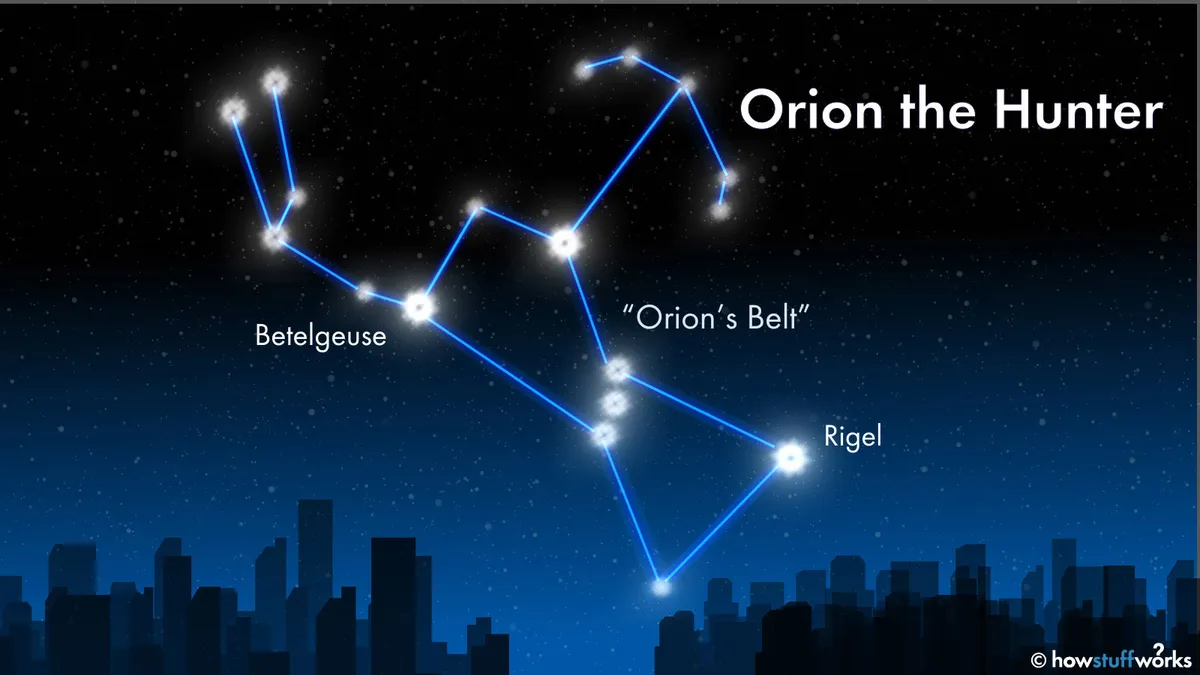
The Orion Star, specifically Betelgeuse, stands out as one of the most remarkable celestial objects visible in the night sky. Located in the constellation Orion, Betelgeuse is a red supergiant star that significantly contributes to the constellation’s distinct appearance. This massive star is situated in Orion’s left shoulder, forming one of the four main stars that outline the hunter’s figure in the sky.
Betelgeuse’s prominence is largely due to its immense size and luminosity. As a red supergiant, it has expanded to a size that is many times greater than our Sun. Estimates suggest that Betelgeuse’s radius is approximately 1,000 times that of the Sun, making it one of the largest stars known. Its expansive size and relative proximity to Earth allow it to shine brightly, making it one of the top ten brightest stars visible from our planet. The star’s distinctive reddish color, which comes from its cooler surface temperature compared to other stars, adds to its striking appearance.
The distance of Betelgeuse from Earth is approximately 640 light-years, although this measurement has a degree of uncertainty due to the challenges in precisely gauging distances to such distant stars. Despite this distance, Betelgeuse is easily observable with the naked eye, especially during the winter months when the constellation Orion is prominent in the evening sky.
Betelgeuse is also famous for its variability. It is a semi-regular variable star, meaning its brightness changes over time. These variations are a result of complex processes occurring within the star, including pulsations of its outer layers. The star’s brightness can fluctuate significantly, sometimes by as much as a factor of two, adding to its intrigue and importance in astronomical studies.
The future of Betelgeuse is a subject of great interest. As a red supergiant, it is nearing the end of its life cycle. Scientists predict that Betelgeuse will eventually undergo a supernova explosion, a spectacular event that will briefly outshine the entire galaxy. This explosion will mark the final stages of the star’s evolution, contributing valuable information to our understanding of stellar life cycles and cosmic phenomena.
In summary, the **Orion Star** Betelgeuse is a fascinating object of study due to its immense size, bright luminosity, and variability. Its role in the constellation Orion, coupled with its impending fate as a potential supernova, makes it a key subject in the field of astronomy.







