
Summary: While both BI and BA leverage data, BI focuses on understanding current performance through reports and dashboards. BA dives deeper, using statistical models to predict future trends and optimize decision-making for growth.
Introduction
In today’s data-driven world, businesses are constantly bombarded with information. But how do you turn this data into actionable insights that drive growth and success? This is where Business Intelligence (BI) and Business Analytics (BA) come in.
While these terms are often used interchangeably, there are key differences between them. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for businesses looking to leverage their data effectively.
Defining Business Intelligence (BI)
Business Intelligence (BI) can be thought of as the foundation for data-driven decision making. It’s a set of methodologies, architectures, and tools that enable businesses to gather, store, access, and analyze data to gain a comprehensive understanding of their operations.
BI focuses on presenting historical and present data in an easily digestible format, allowing users to answer questions like:
What are our top-selling products?
What are our current sales trends?
How are our marketing campaigns performing?
Key Components of BI
Data Warehousing: A central repository that stores historical data from various sources within an organization.
Data Extraction, Transformation, and Loading (ETL): The process of extracting data from various sources, transforming it into a consistent format, and loading it into the data warehouse.
Data Analysis and Reporting Tools: Software applications that allow users to query the data,
create reports, and visualize trends.
Dashboards and Scorecards: Real-time or near-real-time visual representations of key metrics and performance indicators.
Primary Functions of BI
Data Visualization: BI tools translate complex data sets into easy-to-understand charts, graphs, and dashboards. This allows users to identify trends, patterns, and outliers quickly.
Reporting and Analysis: BI enables users to generate reports that answer specific business questions. These reports can be static or interactive, allowing for deeper analysis.
Performance Monitoring: BI helps businesses track key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure progress towards goals and identify areas for improvement.
Improved Decision Making: By providing clear and concise insights into business operations, BI empowers users to make informed decisions based on data, not gut feeling.
Defining Business Analytics (BA)
Business Analytics (BA) builds upon the foundation of BI. It’s a more advanced practice that uses statistical models and techniques to uncover hidden patterns, trends, and relationships within data. BA goes beyond simply describing what’s happening to answer the “why” and “what if” questions. It helps businesses:
Predict future outcomes
Identify potential risks and opportunities
Develop data-driven strategies for growth
Optimize processes and resource allocation
Key Components of BA
By combining the following key components, Business Analytics empowers you to go beyond simply understanding what’s happening to uncover the “why” and “what if” questions hidden within your data. Here is the breakdown of the same:
Statistical Modeling
This component focuses on applying statistical techniques to data to identify patterns, relationships, and trends. Statistical models can be used for various purposes in BA, such as:
Regression Analysis: This technique helps understand the relationship between one dependent variable (what you’re trying to predict) and one or more independent variables (factors that influence the dependent variable). It allows you to estimate how much a change in the independent variable will affect the dependent variable.
Time Series Analysis: This technique focuses on analyzing data collected over time to forecast future trends and seasonality. For example, a company might use time series analysis to predict future sales based on historical sales data.
Hypothesis Testing: This technique helps determine if a particular hypothesis about a population is likely to be true based on sample data. For instance, a marketing team might use hypothesis testing to determine if a new ad campaign has a statistically significant impact on sales.
Data Mining
Data mining involves extracting hidden patterns and knowledge from large datasets that might not be readily apparent through traditional analysis techniques. Here are some common data mining techniques used in BA:
Classification: This technique categorizes data points into predefined groups based on their characteristics. An e-commerce company might use classification to segment customers based on their purchase history.
Clustering: This technique groups data points together based on their similarities, helping uncover hidden patterns and relationships within the data. For example, a bank might use clustering to identify groups of customers with similar financial risk profiles.
Association Rule Learning: This technique discovers relationships between different variables within a dataset. A grocery store might use association rule learning to identify products that are frequently bought together, allowing them to optimize product placement.
Machine Learning (ML)
Machine Learning algorithms learn from data without being explicitly programmed. These algorithms can then be used to make predictions about future events or customer behaviour. Commonly used ML techniques in BA include:
Decision Trees: These algorithms create tree-like structures that classify data based on a series of sequential questions.
Support Vector Machines (SVMs): These algorithms create hyperplanes that separate data points into distinct categories.
Neural Networks: Inspired by the human brain, these complex algorithms learn from data and can identify complex patterns and relationships.
Data Visualization
While data visualization is a key component of BI as well, BA often utilizes more advanced visualization techniques to present complex data insights effectively. These techniques include:
Interactive Dashboards: These dynamic dashboards allow users to drill down into data and explore different dimensions, providing a deeper understanding of the information.
Predictive Modeling Visualization: Techniques like heatmaps and treemaps help visualize the relationships between variables and the impact of different factors on the predicted outcome.
Primary Functions of BA
By leveraging statistical modelling and machine learning techniques, BA can transform historical data into a crystal ball, providing businesses with invaluable insights into what lies ahead. Let’s delve deeper into the world of predictive analytics and explore how it empowers businesses to make data-driven decisions for a more successful future.
Predictive Analytics
BA uses historical data to forecast future trends, allowing businesses to anticipate changes in the market or customer behavior. For instance, a retail company might use BA to predict demand for specific products during the holiday season.
Prescriptive Analytics
It goes beyond simple prediction to suggest optimal courses of action based on data analysis. Imagine a company analyzing customer churn data to identify factors that contribute to customer dissatisfaction. BA can then recommend strategies to address these factors and retain customers.
Risk Assessment
BA helps businesses identify and mitigate potential risks by analyzing historical data and industry trends. An insurance company might use BA to assess the risk of policyholders filing claims.
Customer Segmentation
Business Analytics helps businesses segment their customer base into distinct groups with similar characteristics and behaviors. This allows for targeted marketing campaigns and improved customer satisfaction. For example, a clothing retailer might segment its customers by age, gender, and purchase history to create targeted email campaigns.
Key Differences Between BI and BA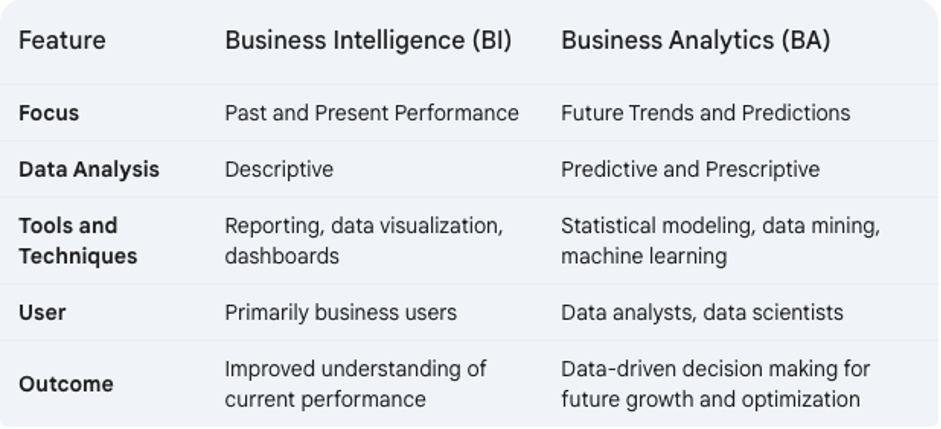
Choosing Between BI and BA
In many cases, BI and BA work best when used together. BI provides the foundation for understanding your current state, while BA helps you leverage that understanding to make better decisions about the future. The choice between BI and BA depends on your specific needs. Here’s a breakdown to help you decide:
Need BI if:
- You need a clear picture of your current performance.
- You want to track key metrics and identify trends.
- You want to empower business users with self-service analytics.
- You have a large volume of data that needs to be organized and easily accessible.
Need BA if:
- You want to predict future outcomes and make data-driven forecasts.
- You want to identify root causes of problems and optimize processes.
- You want to develop data-driven strategies for growth and innovation.
- You have a team of data analysts or data scientists who can leverage advanced statistical techniques.
Here’s an analogy: Imagine BI as the rearview mirror of your car, giving you a clear view of where you’ve been. BA is like the windshield, helping you see where you’re going and navigate the road ahead.
Conclusion
In today’s data-driven world, both BI and BA are essential tools for businesses of all sizes. By understanding the key differences between these two disciplines, you can make informed decisions about how to leverage your data to gain a competitive advantage.
BI empowers you to understand your current situation, while BA equips you to predict future trends and make data-driven decisions for growth and success. Remember, BI is the foundation, and BA is the strategy builder. Together, they form a powerful combination for unlocking the true potential of your data.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Difference Between BI and BA?
BI provides a rearview mirror view of your business, analyzing past and present data. BA acts like a windshield, using data to predict future trends and make data-driven decisions.
When Should I Use BI?
Use BI if you need clear insights into current performance, want to track key metrics, or empower business users to analyze data.
When Should I Use BA?
Use BA if you want to predict future trends, identify root causes of problems, or develop data-driven strategies for growth and innovation.







