Introduction
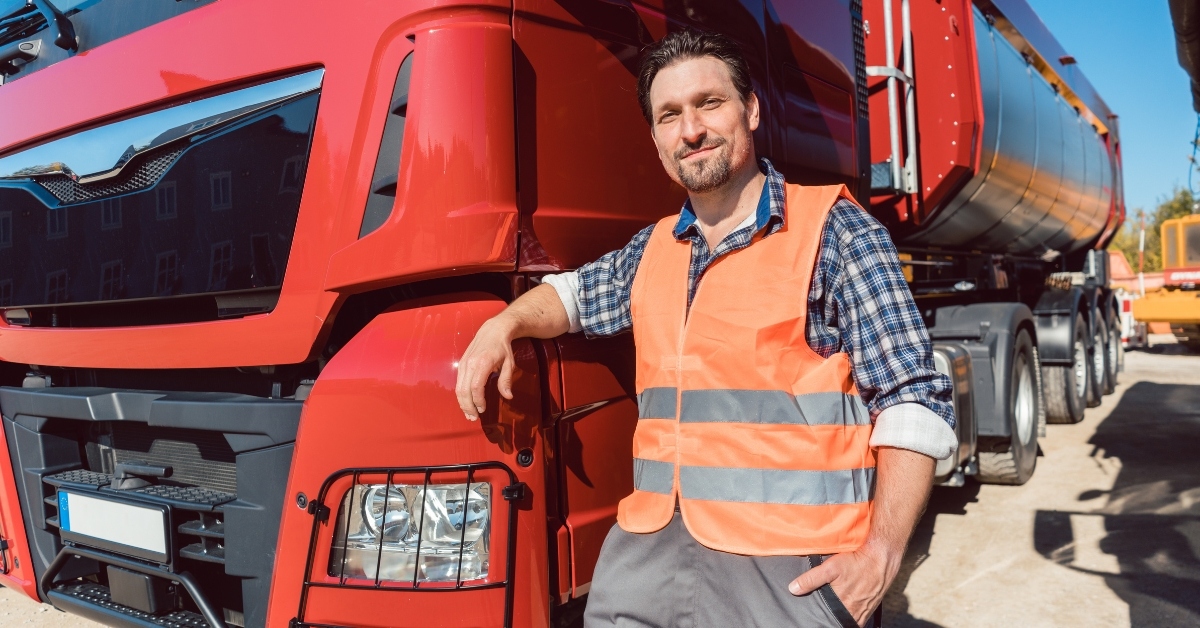
In the world of commercial driving, safety is paramount. Ensuring that drivers are not under the influence of drugs is a critical aspect of maintaining road safety. That’s where drug testing protocols come into play. This article delves into the ins and outs of drug testing for commercial drivers, offering a comprehensive guide to what you need to know.
Understanding the Legal Framework
Federal Regulations
The U.S. Department of Transportation (DOT) and the Federal Motor Carrier Safety Administration (FMCSA) set the federal regulations for drug testing commercial drivers. These regulations are designed to ensure that all drivers are fit for duty and to enhance public safety.
DOT Regulations and Their Impact
DOT regulations require commercial drivers to undergo drug and alcohol testing at specific points, such as pre-employment, randomly during employment, and post-accident. These rules are stringent and non-negotiable, aimed at preventing impaired driving on the roads.
FMCSA Requirements
FMCSA enforces regulations that include a comprehensive drug and alcohol testing program. This program includes testing for substances like marijuana, cocaine, opioids, amphetamines, and phencyclidine (PCP).
State Regulations
While federal laws provide a baseline, state regulations can vary and sometimes impose additional requirements on commercial drivers.
Variations Across States
Different states may have unique laws regarding the substances tested and the thresholds for what constitutes a positive test. It’s crucial for drivers to be aware of these variations, especially if they operate across state lines.
Compliance with State Laws
Staying compliant with both federal and state laws is essential. Ignorance of these laws can lead to severe penalties, including the suspension of a commercial driver’s license (CDL).
Types of Drug Tests
Urine Testing
Urine testing is the most common method used in drug testing for commercial drivers. It’s cost-effective and can detect a wide range of substances.
Common Drugs Detected
Urine tests can detect drugs like marijuana, cocaine, amphetamines, opioids, and PCP. It’s a reliable method for identifying recent drug use.
Pros and Cons of Urine Testing
While urine tests are widely used, they have their limitations. They can sometimes produce false positives, and they have a relatively short detection window compared to other testing methods.
Hair Follicle Testing
Hair follicle testing is another method used in drug testing. It involves analyzing a small sample of hair for traces of drug metabolites.
Detection Window
Hair tests have a much longer detection window than urine tests, often up to 90 days. This makes them suitable for detecting long-term drug use.
Accuracy and Limitations
While highly accurate, hair tests are more expensive and may not detect very recent drug use. They are also less invasive than blood tests but more so than urine or saliva tests.
Saliva Testing
Saliva testing, also known as oral fluid testing, is less invasive and can be done quickly.
How It Works
Saliva tests detect drug metabolites in the saliva, which can be present shortly after drug use. They are commonly used for detecting recent use of substances.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Saliva tests are non-invasive and easy to administer. However, they have a shorter detection window and may not detect all substances as effectively as other methods.
Blood Testing
Blood testing is the most invasive and is usually reserved for specific situations, such as post-accident testing.
When Is It Used?
Blood tests are often used when there is a need for precise measurement of the drug levels in the body, such as in cases of suspected impairment.
Precision and Invasiveness
Blood tests are highly accurate but are more invasive than other methods. In addition, they cost more and take longer to administer.
The Testing Process
Pre-Employment Testing
Before being hired, commercial drivers must undergo drug testing. This is a mandatory requirement to ensure that the driver is fit for duty.
What Employers Look For
Employers look for the presence of drugs and alcohol in the driver’s system. A positive test can disqualify a candidate from employment.
Legal Implications
Failing a pre-employment drug test can have serious legal implications, including disqualification from certain types of work and potential legal action.
Random Testing
Random testing is conducted without prior notice and can occur at any time during a driver’s employment.
Frequency and Selection Criteria
The frequency of random tests is determined by DOT regulations, and the selection process must be random. This ensures fairness and prevents any form of bias.
Handling Positive Results
If a driver tests positive, they may be removed from duty immediately and must undergo a return-to-duty process, which includes counseling and additional testing.
Post-Accident Testing
After an accident, drug testing may be required to determine if the driver was impaired.
Triggers for Testing
Post-accident testing is triggered by specific criteria, such as fatalities, bodily injury requiring medical attention, or significant property damage.
Legal and Safety Considerations
These tests are crucial for legal proceedings and insurance claims. They help establish whether the driver was under the influence at the time of the accident.
Reasonable Suspicion Testing
Reasonable suspicion testing occurs when there is a legitimate reason to believe that a driver is under the influence of drugs or alcohol.
Identifying Suspicious Behavior
Suspicious behavior might include erratic driving, physical symptoms of impairment, or a sudden change in demeanor.
Ensuring Fairness and Privacy
Employers must ensure that reasonable suspicion testing is conducted fairly and respects the driver’s privacy. They must document the reasons for testing to avoid legal issues.
Return-to-Duty Testing
Drivers who have previously tested positive must undergo return-to-duty testing before resuming work.
Steps for Reinstatement
The return-to-duty process involves completing a substance abuse program and passing a return-to-duty drug test. It’s a rigorous process that ensures the driver is fit to return to work.
Monitoring Compliance
Even after returning to duty, drivers may be subject to follow-up testing to ensure they remain drug-free.
Consequences of Failing a Drug Test
Immediate Consequences
Failing a drug test can lead to immediate suspension or termination from employment. The driver’s CDL may also be temporarily suspended.
Suspension and Termination
Drivers who fail a test are typically removed from duty and may be terminated, depending on company policies and the severity of the offense.
Legal Ramifications
The legal consequences of failing a drug test can be severe, including fines, legal action, and permanent loss of a CDL.
Legal Penalties and Fines
Depending on the circumstances, drivers may face legal penalties, including fines and potential jail time, especially if the failed test is associated with a serious accident.
Impact on Career
A failed drug test can have long-term implications for a driver’s career. It can limit future job opportunities and damage their professional reputation.
Long-Term Consequences and Record
A failed test can remain on a driver’s record for several years, affecting their ability to find employment in the industry. It can also impact their personal life, as substance abuse issues often carry a social stigma.
Tips for Drivers to Stay Compliant
Knowing Your Rights and Responsibilities
Understanding your rights and responsibilities as a commercial driver is crucial. This includes knowing the substances that are prohibited and the legal implications of drug use.
Staying Informed About Medications and Substances
Some medications can cause false positives on drug tests. It’s essential to stay informed about the substances you consume and to disclose any prescriptions to your employer.
Resources for Substance Abuse Help
If you’re struggling with substance abuse, resources are available to help you. Many companies offer Employee Assistance Programs (EAPs) that provide support and counseling.
Conclusion
Drug testing protocols for commercial drivers are stringent and necessary for maintaining road safety. By understanding the different types of tests, the testing process, and the consequences of failing a test, drivers can better navigate these regulations and maintain their careers. Staying informed and compliant is key to ensuring a safe and successful career in commercial driving.