How retina scan is used to diagnose dementia?
AI Tools for Detecting Dementia: Unveiling the Future of Neurological Diagnosis
Introduction to Dementia Detection Through AI
Dementia, a group of symptoms that affect memory, thinking, and social abilities, has long been a challenge to diagnose early. However, artificial intelligence (AI) is now at the forefront of innovative solutions to detect early signs of this debilitating condition. Researchers have recently developed AI-powered tools capable of analyzing retinal scans to predict neurological diseases like dementia. This breakthrough highlights the interconnectedness of the brain and eyes and underscores the potential of technology in transforming healthcare.
Understanding Dementia and Its Stages
What is Dementia?
Dementia isn’t a single disease but a term that encompasses a range of cognitive impairments. While memory loss is a hallmark symptom, dementia can manifest in various forms, including:
- Alzheimer’s Disease: Marked by progressive memory decline and cognitive deterioration.
- Vascular Dementia: Often associated with behavioral changes and difficulties in decision-making.
Early Symptoms of Dementia
Early detection is critical, yet the symptoms of dementia often overlap with other conditions, making diagnosis complex. Common early signs include:
- Forgetfulness beyond normal aging.
- Difficulty concentrating on tasks.
- Challenges in understanding speech or communication.
- Changes in behavior, such as irritability or extreme anxiety.
The Role of AI in Early Dementia Detection
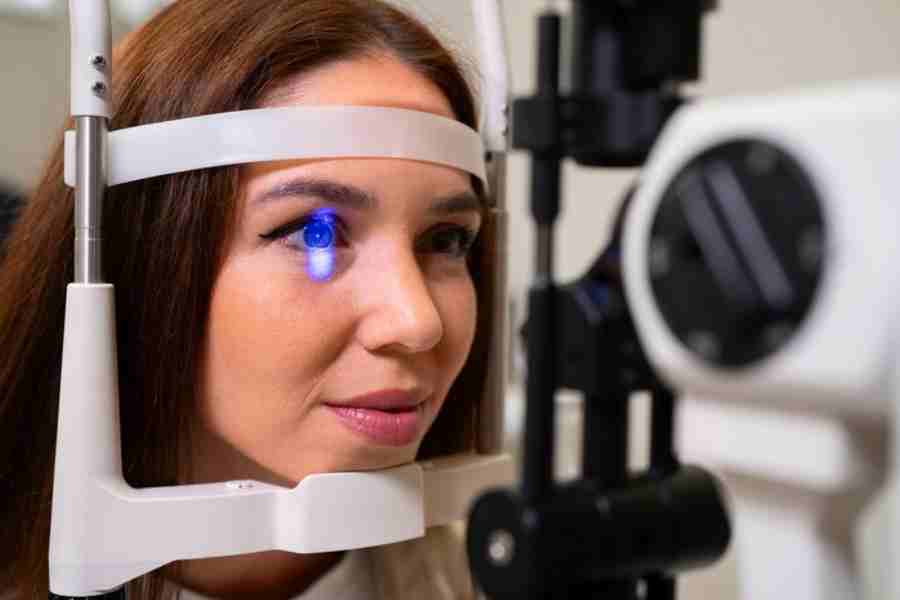
The Retina as a Window to the Brain
The retina, a thin layer of nerve cells and blood vessels in the eye provides a unique view of neurological health. Researchers from Edinburgh University and Glasgow Caledonian University discovered that subtle changes in the retina and optic nerve can indicate early signs of dementia, even before symptoms appear.
How AI Analyzes Retinal ScansAI-powered tools use sophisticated algorithms to analyze high-resolution images of the retina. These algorithms detect microscopic changes in:
- Nerve cells and their interactions.
- Blood vessel structures linked to the brain’s health.
By interpreting these data points, AI tools can predict the likelihood of developing conditions like Alzheimer’s or vascular dementia.
The Science Behind Retinal Scanning
Retinal scans are non-invasive and quick, making them a convenient diagnostic tool. They capture intricate details about:
- Blood vessel density and irregularities.
- Patterns of cell degeneration associated with brain aging.
The Connection Between Dementia and Behavioral Changes
From Forgetfulness to Aggression
Psychologists emphasize that dementia-related behavioral changes often go unnoticed until the condition progresses. These changes may include:
- Increased anxiety or excessive worry.
- A loss of interest in previously enjoyed activities.
- Difficulty performing routine tasks due to impaired judgment.
How AI Tools Address Behavioral Symptoms
AI not only detects physical markers but can also analyze patterns in behavior, speech, and decision-making. This dual approach helps doctors identify both physical and psychological symptoms early on.
Benefits of AI in Dementia Diagnosis
Enhanced Precision and Speed
Traditional diagnostic methods for dementia rely heavily on subjective evaluations and lengthy assessments. AI tools offer:
- Greater accuracy by analyzing minute retinal changes.
- Faster results compared to conventional neurological tests.
Accessibility and Non-Invasive Methods
Unlike brain scans or invasive procedures, AI-powered retinal diagnostics are more accessible and less intimidating for patients. This increases the likelihood of early detection in broader populations.
Potential for Predicting Other Neurological Diseases
AI’s ability to detect retinal changes extends beyond dementia. Studies show that retinal scans can also reveal early signs of:
- Parkinson’s disease.
- Multiple sclerosis.
- Stroke risks.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Limitations of AI in Medical Diagnosis
Despite its promise, AI technology is not without challenges. These include:
- The need for large, diverse datasets to improve accuracy.
- Potential biases in algorithm design that could lead to disparities in diagnosis.
Data Privacy and Security Concerns
Retinal scans involve sensitive health data, raising questions about how this information is stored and shared. Ethical considerations must guide the development and deployment of AI tools to protect patient privacy.
The Future of AI in Dementia Care
Advancing AI Algorithms
Future developments aim to make AI tools even more accurate by incorporating additional data, such as genetic markers and lifestyle factors, into their analysis.
Integration with Healthcare Systems
Seamless integration of AI tools into existing healthcare systems could revolutionize how doctors diagnose and treat dementia. Collaborative efforts between AI developers and healthcare providers will be essential.
Personalized Treatment Plans
AI’s predictive capabilities may eventually enable tailored treatment plans based on an individual’s unique risk factors, ensuring more effective care.
Conclusion: A New Era in Neurological Diagnosis
The advent of AI tools for dementia detection marks a significant milestone in medical science. By leveraging advanced algorithms to analyze retinal scans, scientists are making early diagnosis more accessible and accurate than ever before. While challenges remain, the potential to transform healthcare and improve patients’ lives is immense.
As researchers continue to refine these tools, the dream of detecting dementia before it becomes debilitating is fast becoming a reality. This innovation offers hope not just for dementia patients but for the broader field of neurological health.
By focusing on early detection, accessible technology, and ethical considerations, AI is not just detecting disease—it’s paving the way for a healthier future.







