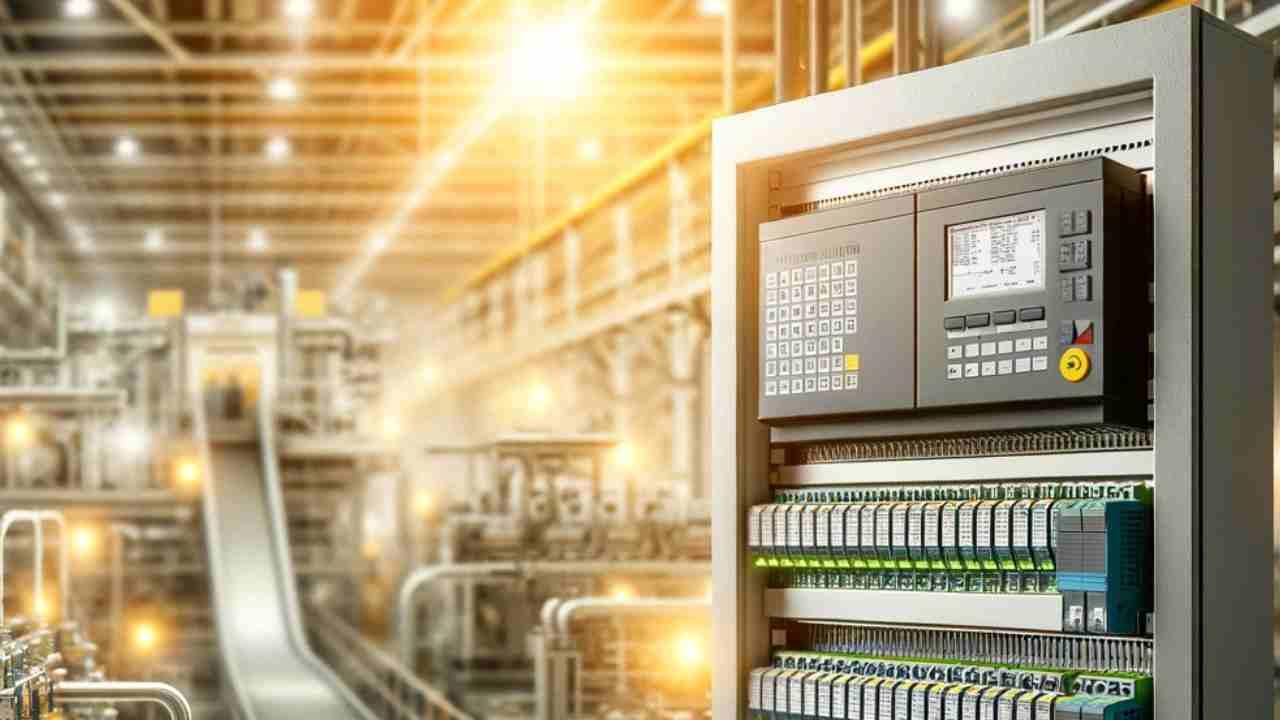
The automation of factories has emerged as a fundamental element of contemporary manufacturing, providing improved efficiency, accuracy, and safety. Central to this evolution are Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs), which function as the central processing units of automated systems. These robust digital computers are specifically engineered to manage intricate industrial processes, guaranteeing the smooth functioning of machinery and systems.
The Role of PLCs in Factory Automation
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) play a crucial role in the realm of factory automation, offering essential control and adaptability for a diverse range of industrial applications. These controllers facilitate the automation of tasks that were previously executed manually, including assembly line operations, machinery functions, and quality assurance processes. Through the automation of these activities, PLCs enable manufacturers to enhance productivity.
Key Features of PLCs in Automation
Real-Time Control:
A key benefit of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) is their capacity to deliver real-time management of industrial operations. This capability is essential in settings where timing and accuracy are paramount, such as in the automotive manufacturing sector or chemical processing facilities. PLCs are capable of swiftly processing inputs and outputs, thereby guaranteeing that machinery functions in complete harmony.
Scalability:
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) offer significant scalability, enabling manufacturers to adjust or enhance their automation systems as required. This adaptability is crucial in sectors that necessitate regular modifications to production lines or equipment setups. Regardless of whether the operation is a modest, single-machine setup or an extensive manufacturing plant, PLCs can be tailored to meet the unique requirements of the operation.
Durability:
Industrial settings frequently present challenging conditions characterized by extreme temperatures, dust, and vibrations. Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) are engineered to endure these environments, ensuring their reliability for prolonged use. Their durable construction guarantees functionality in situations where conventional computers may not perform adequately.
Ease of Programming:
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) are equipped with intuitive programming languages, including Ladder Logic, which is derived from relay logic diagrams. This design facilitates the programming and troubleshooting processes for technicians and engineers. Additionally, numerous PLCs provide sophisticated programming alternatives such as Function Block Diagrams (FBD) and Structured Text (ST), addressing the requirements of more intricate automation tasks.
Applications of PLCs in Factory Automation
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) find applications across various sectors, such as automotive, food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, and oil and gas. In the automotive sector, for instance, PLCs oversee robotic arms responsible for vehicle assembly, guaranteeing accuracy and uniformity in each manufactured unit. Similarly, in the food and beverage sector, PLCs regulate processes such as mixing, filling, and packaging, which demand rigorous compliance with quality and hygiene regulations.
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) are essential components in the realm of factory automation, enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and safety across multiple sectors. As technological advancements progress, the significance of PLCs will increase, further influencing the future landscape of manufacturing. By incorporating emerging technologies and responding to evolving challenges, PLCs will continue to lead the way in industrial automation, facilitating the development of smarter and more efficient manufacturing environments.







