Root canals are a common dental procedure aimed at saving a tooth that is severely infected or damaged. Understanding the causes, symptoms, recovery, and treatment process of a root canal can help alleviate any fears or concerns you might have. This comprehensive guide will cover everything you need to know about root canals, helping you make informed decisions about your dental health.
What is a Root Canal?
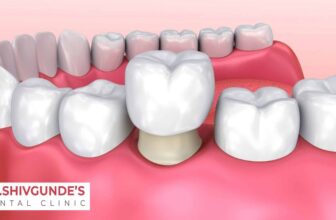
A root canal is a dental procedure that involves removing the infected or damaged pulp from inside a tooth, cleaning and disinfecting the space, and then filling and sealing it.
The pulp is the soft tissue inside the tooth that contains nerves, blood vessels, and connective tissue. When it becomes infected or inflamed due to deep decay, repeated dental procedures, or injury, it can cause severe pain and lead to an abscess if left untreated.
Causes of Root Canal Infections
Several factors can contribute to the need for a root canal, including:
- Deep Decay: Untreated cavities that reach the pulp can cause bacterial infection and inflammation.
- Repeated Dental Procedures: Multiple procedures on the same tooth can stress the pulp and lead to infection.
- Cracked or Chipped Tooth: Injuries that cause cracks or chips can expose the pulp to bacteria.
- Trauma: A blow to the tooth, even without visible cracks, can damage the pulp over time.
- Large Fillings: Large or deep fillings can sometimes irritate or expose the pulp, leading to infection.
Symptoms Indicating the Need for a Root Canal
Identifying the symptoms early can help prevent further complications and the need for more extensive treatments. Common symptoms that may indicate the need for a root canal include:
- Severe Toothache: Persistent pain that can range from a dull ache to sharp, severe pain, often worsening when chewing or applying pressure.
- Prolonged Sensitivity: Lingering sensitivity to hot or cold temperatures, even after the source of the temperature is removed.
- Swollen Gums: Swelling around the affected tooth, sometimes accompanied by a small bump (abscess) on the gums.
- Discoloration: Darkening of the tooth, indicating internal damage or decay.
- Tenderness: Tenderness or discomfort in the surrounding gums and jaw.
The Root Canal Treatment Process
Understanding the root canal procedure can help alleviate any anxiety you may have. The treatment generally involves several steps:
- Diagnosis and X-rays: The dentist will examine your tooth and take X-rays to determine the extent of the infection and plan the treatment.
- Local Anesthesia: The affected area is numbed using local anesthesia to ensure a painless procedure.
- Access Opening: The dentist creates an opening in the crown of the tooth to access the infected pulp.
- Pulp Removal: The infected or damaged pulp is carefully removed using specialized instruments.
- Cleaning and Disinfecting: The root canals are cleaned, disinfected, and shaped to prepare for the filling.
- Filling and Sealing: The cleaned canals are filled with a biocompatible material (gutta-percha) and sealed to prevent future infection.
- Restoration: After the root canal, a crown or filling is placed to restore the tooth’s structure and function.
Recovery After a Root Canal
Recovery from a root canal is typically smooth, with most patients returning to normal activities within a day or two. Here are some tips to ensure a quick and comfortable recovery:
- Pain Management: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help manage any discomfort after the procedure.
- Avoid Chewing on the Treated Tooth: Avoid chewing on the treated tooth until it is fully restored with a crown or filling to prevent damage.
- Maintain Oral Hygiene: Continue regular brushing and flossing, but be gentle around the treated area.
- Follow-Up Visits: Attend follow-up appointments to ensure proper healing and placement of the final restoration.
Potential Complications
While root canals are highly successful, there can be potential complications. These may include:
- Re-infection: If the tooth is not properly sealed or new decay develops, re-infection can occur.
- Fracture: A treated tooth is more brittle and may fracture if not properly restored.
- Persistent Symptoms: Occasionally, symptoms may persist, requiring further treatment or retreatment.
Preventing Root Canal Issues
Prevention is always better than cure. Here are some tips to reduce the risk of needing a root canal:
- Maintain Good Oral Hygiene: Brush and floss regularly to prevent decay and gum disease.
- Regular Dental Check-Ups: Visit your dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings to catch problems early.
- Avoid Hard Foods: Avoid chewing on hard foods or objects that can crack or chip your teeth.
- Wear a Mouthguard: If you play sports or grind your teeth at night, wearing a mouthguard can protect your teeth from injury.
Conclusion
A root canal is a highly effective treatment for saving a damaged or infected tooth. Understanding the causes, symptoms, treatment process, and recovery can help you feel more comfortable and informed about the procedure.
If you experience any symptoms of a root canal infection, it’s essential to seek prompt dental care to prevent further complications and preserve your oral health. Remember, maintaining good oral hygiene and regular dental check-ups are key to preventing dental issues and ensuring a healthy, beautiful smile.
For best root canal treatment visit- Root Canal Treatment in Borivali West