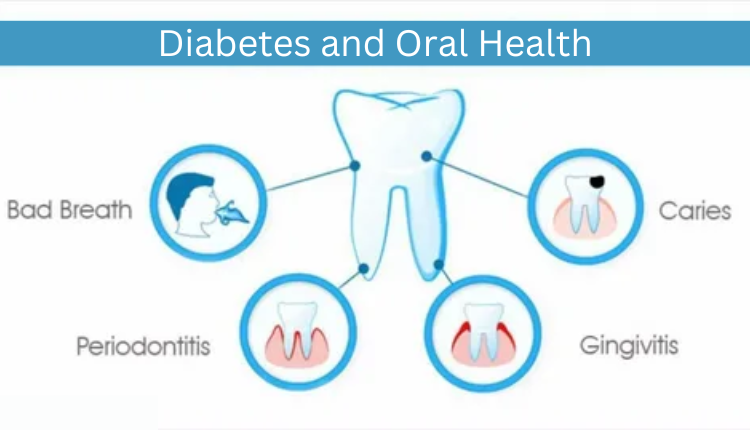
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how the body processes blood sugar (glucose). It can have significant implications for oral health, as fluctuations in blood sugar levels can increase the risk of various dental and gum problems. Understanding the impact of diabetes on oral health is crucial for effectively managing both conditions.
For reliable care, visit dental clinic in Borivali West by Dr. Shreya Shetty. Offering expert treatments, modern technology, and a welcoming environment for all your dental needs.
How Diabetes Affects Oral Health
Diabetes can influence oral health in several ways:
1. Gum Disease (Periodontal Disease):
- Increased Risk: People with diabetes are at a higher risk of developing gum disease. Poor blood sugar control can lead to a buildup of plaque and bacteria on the teeth, which can cause gingivitis (gum inflammation) and progress to periodontitis (severe gum disease).
- Symptoms: Symptoms include swollen, tender gums, bleeding while brushing or flossing, and receding gums. If left untreated, periodontitis can lead to bone loss and eventual tooth loss.
2. Dry Mouth (Xerostomia):
- Reduced Saliva Production: Diabetes can cause decreased saliva production, leading to dry mouth. Saliva helps wash away food particles and neutralize bacteria’s acids. A dry mouth increases the risk of tooth decay, gum disease, and oral infections.
- Symptoms: Dry mouth symptoms include a dry feeling in the mouth, frequent thirst, difficulty swallowing or speaking, and cracked lips.
3. Thrush (Oral Candidiasis):
- Yeast Infections: People with diabetes are more prone to oral fungal infections like thrush, which is caused by the overgrowth of Candida albicans yeast in the mouth.
- Symptoms: Symptoms include white patches on the tongue, inner cheeks, roof of the mouth, and throat. Thrush can cause discomfort, a burning sensation, and difficulty swallowing.
4. Delayed Wound Healing:
- Impaired Immune Response: Diabetes can weaken the body’s immune system, making it harder to fight infections, including oral infections. This can result in slower healing of oral wounds, such as cuts, sores, or oral surgery sites.
5. Increased Risk of Tooth Decay:
- Higher Susceptibility: Fluctuations in blood sugar levels can increase the risk of tooth decay (cavities). Elevated sugar levels in saliva can promote the growth of bacteria that produce acids, which attack tooth enamel.
- Importance of Oral Hygiene: Maintaining good oral hygiene, including regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups, is crucial for preventing cavities.
Managing Oral Health with Diabetes
Effective management of diabetes is essential for minimizing its impact on oral health:
1. Control Blood Sugar Levels:
- Monitor Blood Glucose: As your healthcare provider advises, regularly monitor blood sugar levels. Stable blood glucose levels reduce the risk of complications, including oral health problems.
- Follow Treatment Plan: Adhere to your diabetes treatment plan, which may include medications, insulin therapy, diet, and exercise.
2. Practice Good Oral Hygiene:
- Brush and Floss Regularly: Brush your teeth at least twice daily with fluoride toothpaste and floss daily. Pay attention to cleaning along the gum line to remove plaque.
- Use Mouthwash: Rinse with an antimicrobial mouthwash to reduce plaque and control gingivitis.
- Visit Your Dentist: Schedule regular dental check-ups and cleanings. Inform your dentist about your diabetes status and any changes in your health.
3. Control Risk Factors:
- Quit Smoking: Smoking increases the risk of gum disease and complications associated with diabetes. Quit smoking to improve both oral and overall health.
- Maintain a Healthy Diet: Eat a balanced diet of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains. Limit sugary foods and drinks that can contribute to tooth decay.
4. Manage Dry Mouth:
- Stay Hydrated: Drink plenty of water daily to alleviate dry mouth symptoms.
- Chew Sugar-Free Gum: Chewing sugar-free gum or sucking on sugar-free candy stimulates saliva production.
5. Communicate with Your Healthcare Team:
- Integrated Care: Coordinate with your healthcare team, including your dentist and diabetes specialist, to ensure comprehensive management of both diabetes and oral health.
Conclusion
Diabetes can significantly impact oral health, increasing the risk of gum disease, dry mouth, thrush, delayed wound healing, and tooth decay. By maintaining good blood sugar control, practicing proper oral hygiene, and seeking regular dental care, individuals with diabetes can reduce the risk of oral health complications. Effective diabetes management and proactive oral health habits contribute to overall well-being and quality of life.
If you have diabetes, prioritize your systemic and oral health by integrating dental care into your diabetes management plan. Regular dental visits and daily oral care routines are key to maintaining a healthy smile despite the challenges of diabetes.